News & Information
Is now the perfect time to sell your gold?
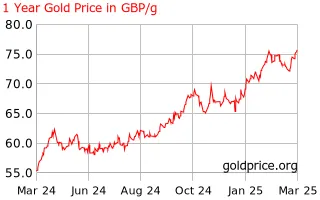
The cash value of gold has been increasing but can it really go higher? Now could be the perfect time to sell your gold, while prices are at an all-time high.
What does the term 'Carat' mean?
Carats are used to express the purity of gold. 100% pure gold is 24 carats, but in practice this is too malleable to be used for jewellery and other metals are added to create alloys with different proportions of gold. This strengthens the material but reduces its value as it contains less gold.
There are some standard carats you might recognise:

- 18 carat gold is 75% pure gold (18 of the 24 units are gold)
- 14 carat gold is 58.3% pure gold (14 of the 24 units are gold)
- 9 carat gold is 37.5% pure gold (9 of the 24 units are gold)
The resulting type of gold depends on what metals are added to the alloy. For example, Rose Gold gets it's pinky colour from adding copper whereas White Gold is achieved by adding a white metal like nickel or zinc.
Why should we recycle gold?
Not only can you make money, recycling old gold reduces the demand for gold mining, which has some serious ecological consequences. Some examples of these include:
- Water contamination: Toxic waste from gold mines can pollute water sources like rivers, lakes, and oceans with heavy metals, acids, cyanide, and petroleum byproducts.
- Soil contamination: Heavy metals from exposed waste rock and tailings can spread through erosion and contaminate the soil.
- Ecosystem destruction: Mining can threaten natural areas and lead to the loss of vegetation.
- Health risks: The byproducts of acid mine drainage (AMD) can make people and animals sick for generations.
- Carbon footprint: The gold industry contributes to global emissions.
- Mercury emissions: Small-scale gold mining in the global south is responsible for 38% of global mercury emissions from human activity.
- Water usage: It takes an average of 265,000 litres of water to produce one kilogram of gold.
It is RecycleOldGold’s mission to get unwanted or unused old gold back into the economy.
Read some related news here
https://www.smithschool.ox.ac.uk/news/stop-mining-new-gold-say-oxford-researchers
XRF Analysis
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation. Other types
of radiation in this category include radio waves, infra-red light, visible
light and ultra-violet light. All electromagnetic radiation travels at the
speed of light and can be represented as a waveform. The distance between two
wave peaks is called the wavelength.
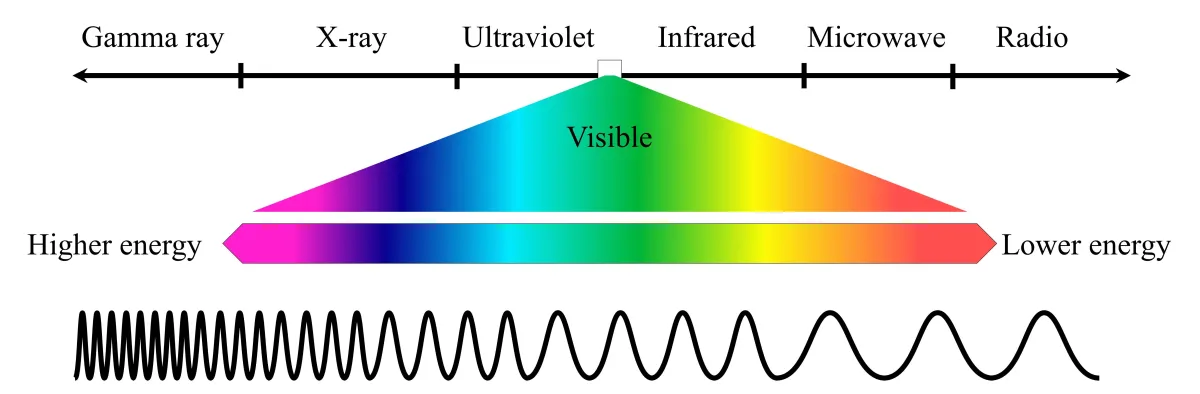
Higher frequency waves have a shorter wavelength and carry
greater energy so are more penetrating. Where the wavelength is less than about
100nm it is also ionising radiation, which means it can make changes to the
atoms it interacts with by removing electrons.
As the electrons are removed, the remaining electrons
reposition themselves and in doing so, give off energy. This phenomenon is
known as X-ray fluorescence and the measurement of the energy produced tells
you what elements the atoms belonged to. It is in this way that you can use an
XRF analyser to accurately determine the composition of an object, or in this
case, how much gold or precious metal is contained in an item.
CUSTOMER CARE
CONTACT US
LEGAL

